Repairing Your Foundation: Complete Guide to Foundation Repair Cost, Crack Repair, and Subsidence Solutions
A sinking or cracked foundation undermines a home’s stability and invites water intrusion, mold and structural failure if left unaddressed. Effective foundation repair combines precise diagnosis with proven methods—underpinning, helical piers, slab jacking, epoxy injection and carbon fibre reinforcement—to restore stability and protect your investment. In this guide you will discover the tell-tale signs of foundation distress, explore common causes and subsidence triggers, compare leading repair techniques, understand local New Jersey cost factors, learn prevention strategies, and see why Effective Basement Solutions is the trusted partner for lasting results.
Key themes covered:
- Identifying visual, functional and water-related warning signs
- Understanding soil movement, drainage flaws and root damage
- Evaluating underpinning, piers, jacking, injection and reinforcement
- Breaking down cost drivers and average repair estimates in New Jersey
- Preventing future damage with drainage, waterproofing and landscaping
- Assessing expertise, process and proof from Effective Basement Solutions
What Are the Common Signs Your Foundation Needs Repair?
Foundation distress manifests through cracks, misaligned openings and moisture issues that compromise structural integrity and safety. Recognising these early prevents costly settlement and basement flooding.
How to Identify Foundation Cracks: Vertical, Horizontal, and Stair-Step Types
Foundation cracks appear in several patterns, each reflecting distinct stress mechanisms and severity levels. Vertical cracks often result from concrete shrinkage or minor settlement, while horizontal and stair-step cracks indicate significant lateral pressure or uneven soil movement.
- Vertical cracks running straight up or down suggest normal curing stress or minor settlement.
- Horizontal cracks parallel to the floor emerge from soil pressure against basement walls.
- Stair-step cracks tracing mortar joints in blocks or brick walls signal differential settlement.
These crack patterns forecast the repair method required and the urgency of stabilisation. Understanding crack orientation leads us to the distinction between minor hairline fissures and structural splits.
What Are the Differences Between Hairline and Structural Foundation Cracks?
Before selecting a repair approach, distinguish superficial hairline cracks from serious structural breaks.
| Crack Type | Width Range | Cause | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hairline Cracks | < 0.3 mm | Concrete shrinkage, minor stress | Epoxy or polyurethane injection seal |
| Structural Cracks | > 0.5 mm | Settlement, hydrostatic pressure | Underpinning or pier stabilisation |
Hairline cracks primarily affect aesthetics and minor moisture seepage, while structural cracks threaten load-bearing integrity and require foundation-level solutions. Recognising this difference guides effective remediation planning.
An Evaluation of the Efficacy of Epoxy Injection for the Repair of Concrete Cracks
The epoxy injection method has been extensively employed for the repair of cracks in concrete structures over the past two decades. This paper elucidates the efficacy of the epoxy injection method in repairing both normal and high-strength reinforced concrete beams. Within the study, the mechanical properties of the repaired beams were assessed, and the findings indicated that epoxy injection can effectively restore the strength and stiffness of cracked concrete beams.
What Functional Issues Indicate Foundation Problems?
Beyond cracks, foundation distress impairs the function of doors, windows and floors, signalling uneven movement and subsidence.
- Sticking or misaligned doors and windows: frames warp or jam when walls shift.
- Sloping or sagging floors: one side of a room feels higher due to soil consolidation.
- Gaps between walls and ceilings or floors: separation indicates shifting loads.
These symptoms often accompany visible cracking and prepare the way to examine moisture’s role in foundation failure.
How Does Water Damage Affect Basement Foundations?
Water intrusion undermines soil bearing capacity and fosters mold, accelerating wall bowing and settlement.
- Persistent basement leaks concentrate hydrostatic pressure behind walls.
- Dampness and efflorescence signal moisture wicking through concrete.
- Mold growth and millboard decay weaken wall surfaces and framing.
Addressing water damage through waterproofing and drainage lays the groundwork for any foundation repair strategy.
What Causes Foundation Damage and Subsidence?
Foundation failure springs from soil movement, water mismanagement and biological or construction flaws that shift load paths and create uneven settlement.
How Do Soil Conditions Like Expansive Clay Cause Foundation Issues?
Expansive clay soils absorb moisture and swell in wet seasons, then shrink in droughts, generating cyclical heave and drop forces on footings. This repeated stress fractures concrete and disturbs load transfer, resulting in cracks and uneven floors. Accounting for clay’s behaviour is crucial when designing underpinning or pier systems to stabilise movement.
Why Is Poor Drainage a Major Factor in Foundation Failure?
Insufficient grading and gutter down-spouts that discharge near footings allow surface water to pool, raising hydrostatic pressure and saturating adjacent soils. Over time this softens soil support and causes lateral wall bowing or downward settlement. Effective site drainage prevents soil over-saturation and readies the structure for durable foundation repair.
How Do Tree Roots and Construction Flaws Contribute to Foundation Damage?
Large roots draw moisture from under slabs and footings, creating dry zones that shrink soils unevenly, while construction errors—like inadequate reinforcement or shallow footings—compound settlement problems. Combining root control with structural reinforcement ensures long-term stability and mitigates repeat subsidence.
What Are the Most Effective Foundation Repair Methods?
Repairing foundation distress demands selecting the appropriate method based on soil conditions, crack severity and structural loads. The leading solutions stabilise, lift or seal compromised sections to restore integrity.
How Does Underpinning Stabilise Sinking Foundations?
Underpinning replaces or extends existing footings with mass concrete or micro-piles to deeper, load-bearing strata. This method transfers structural weight below unstable soils, halting further settlement and realigning the foundation.
| Method | Load Capacity | Installation Depth | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass Concrete | 20–50 kPa | 1.2–2 m | Evenly distributed load beneath slabs |
| Micro-Piles | 50–150 kPa | 2–6 m | Concentrated loads, restricted access |
Underpinning’s strength lies in its adaptability to varying load and site constraints, preparing the foundation for renewed support.
What Are Helical Piers and How Do They Work?
Helical piers consist of screw-like steel shafts that are mechanically driven into stable soil layers. Each pier’s helical flights anchor below shifting soils, enabling precise lifting of settled foundations and enduring resistance to uplift. Installation proceeds with torque monitoring to ensure required capacity is reached before load transfer, offering minimal excavation and rapid load stabilisation.
Experimental Investigation of Grouted Helical Piers for Foundation Rehabilitation
It is hypothesised that these grouted helical pier systems could address foundation issues by providing a stable and reliable foundation support system. Helical piers are a type of deep foundation that is screwed into the ground, similar to a large screw, and can be used to support a variety of structures, including homes and buildings. They are often used in situations where the soil is unstable or where there is a risk of settlement.
How Does Slab Jacking Repair Sunken Concrete Foundations?
Slab jacking, or polyurethane foam injection, lifts settling concrete slabs by injecting expanding foam beneath the slab. The foam fills voids, consolidates loose soils and gently raises the slab back to level. This method is cost-effective for minor to moderate sunken areas and cures quickly, reducing downtime and restoring floor alignment.
When Is Epoxy Injection Used for Foundation Crack Repair?
Epoxy injection seals hairline to medium-width cracks by injecting low-viscosity resin that bonds and restores the structural integrity of concrete. This technique halts water ingress, prevents crack propagation and reinforces the wall along the repaired seam. It is best suited for cracks under 5 mm and where precise alignment is needed.
How Does Carbon Fibre Reinforcement Strengthen Foundation Walls?
Carbon fibre straps affixed to bowed walls provide high-tensile support against lateral soil pressure. The straps adhere with epoxy, distributing loads across broader wall sections without invasive reconstruction. This discreet reinforcement halts further bowing and often eliminates the need for external bracing.
Strengthening Concrete Foundation Beams with Carbon Fibre Composites
For several years, Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) has been gradually replacing steel plates in the reinforcement of concrete structures that are damaged or require increased resistance. It has long been established that the addition of CFRP laminates to structures such as beams and slabs considerably increases their bending and shear strength. However, the behaviour of foundation beams with these reinforcements is not clear. The essential issue in the analysis of reinforced structures with composite materials is to understand the individual behaviour of each material and its interaction with the others. In this paper, the bending and shear strength of concrete foundation beams with CFRP reinforcement are analysed through the study of their load capacity variation and beam deflections. Different height/span beam ratios are considered. The numerical modelling is performed using the Finite Element Method with the Abaqus program. Non-linear models are used for concrete and soil, and a linear elastic model is adopted for composite materials.
How Much Does Foundation Repair Cost in New Jersey?
Estimating foundation repair in New Jersey depends on damage severity, soil conditions and chosen method. Transparent cost breakdowns help homeowners budget and plan remediation.
What Factors Influence Foundation Repair Costs?
Foundation repair expenses reflect multiple variables:
- Extent and type of damage: crack width, wall bowing or settlement depth
- Soil conditions and access: clay vs sandy soils, ease of machine access
- Repair method complexity: underpinning, piers, jacking or injection
- Site preparation and landscaping restoration requirements
Assessing these factors ensures an accurate estimate and prevents unexpected overruns.
What Are the Average Costs for Different Repair Methods?
Introducing typical cost ranges for common repairs in New Jersey:
| Repair Method | Typical Range ($) | Project Scope |
|---|---|---|
| Epoxy Injection | 250–600 | Hairline to minor structural cracks |
| Slab Jacking | 600–1,200 | Sunken slab areas under 1 m² |
| Helical Piers | 2,000–5,000 | Moderate settlement on perimeter footings |
| Underpinning | 4,000–8,000 | Extensive sinking requiring deep support |
These averages guide budgeting decisions and highlight the value of early intervention.
How Can You Get a Free Foundation Repair Estimate?
Securing a complimentary on-site evaluation involves scheduling a professional inspection, soil analysis and diagnostic scan. A certified technician assesses crack patterns, wall deflection and groundwater conditions, then delivers a detailed proposal within days—empowering homeowners with transparent options and cost breakdowns.
How Can You Prevent Future Foundation Damage?
Proactive maintenance reduces the risk of recurring settlement, cracks and water intrusion by addressing environmental factors and reinforcing protective measures.
Why Is Proper Drainage and Grading Essential for Foundation Health?
Sloping terrain away from the foundation and installing gutters that channel water at least 3 m from footings prevents soil saturation. Consistent grading and drain tile systems manage runoff effectively, maintaining uniform soil moisture and eliminating hydrostatic pressure that leads to wall bowing and slab settlement.
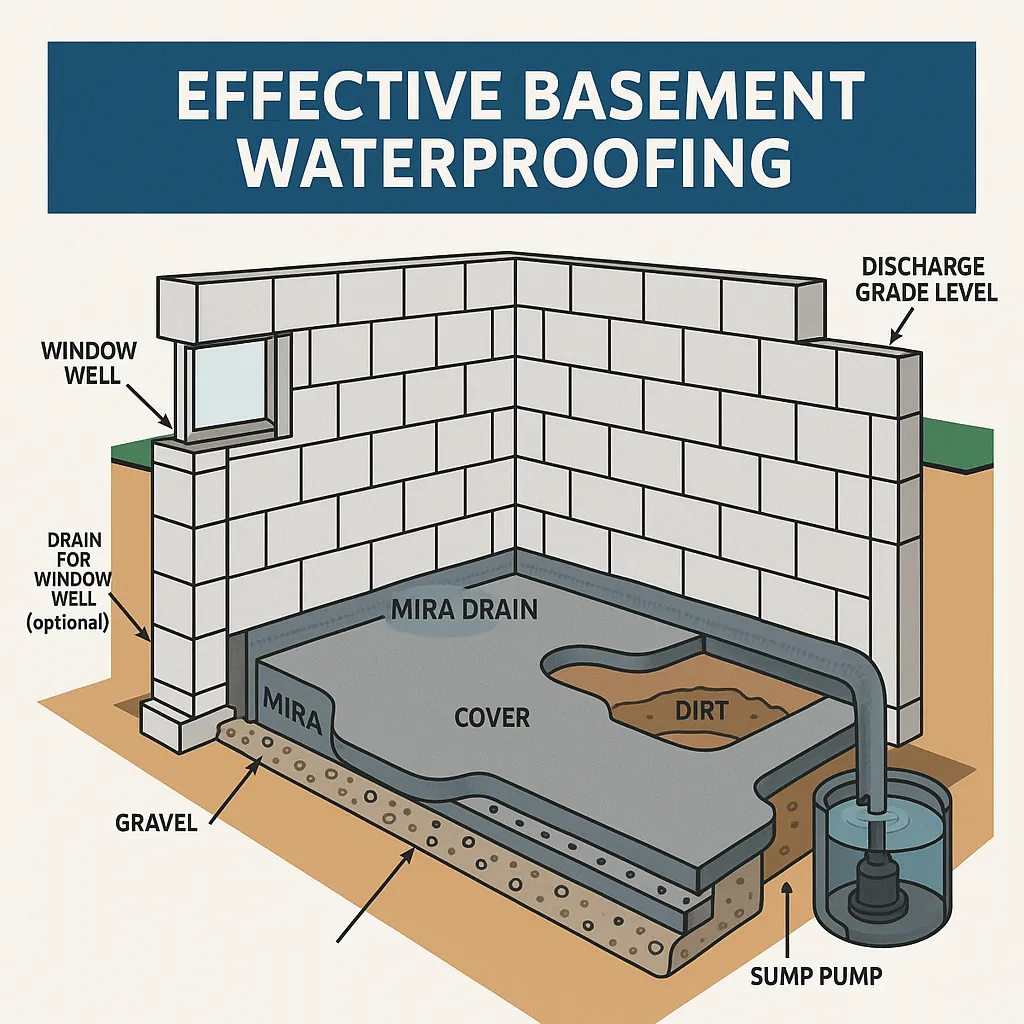
How Does Basement Waterproofing Protect Your Foundation?
Interior and exterior waterproofing membranes, combined with drain tile installation, divert groundwater away from foundation walls. Sealing joints and applying polymer-modified coatings stops moisture at its source, preserving soil stability and reducing freeze-thaw damage that accelerates crack formation.
What Role Does Tree and Shrub Management Play in Foundation Care?
Maintaining a root-free perimeter of at least 1.5 m around the foundation prevents moisture uptake imbalances and root-induced soil shrinkage. Selecting shallow-rooted plants and pruning established trees safeguards soil consistency and avoids uneven settlement beneath footings.
Why Choose Effective Basement Solutions for Your Foundation Repair?
Effective Basement Solutions brings specialised expertise, advanced methods and local New Jersey experience to every project—ensuring durable outcomes and homeowner confidence.
What Expertise and Experience Does Effective Basement Solutions Offer?
With decades of combined experience in structural repairs and geotechnical assessment, our certified technicians diagnose complex foundation issues using resurging technologies—laser scanning, soil testing and moisture monitoring—to design tailored repair plans that address root causes and long-term performance.
What Is the Step-by-Step Foundation Repair Process?
- Inspection & Analysis: Detailed crack mapping, soil evaluation and moisture assessment
- Solution Design: Selecting underpinning, piers, jacking or reinforcement based on site data
- Preparation & Excavation: Securing work area and exposing foundation zones
- Installation & Repair: Executing chosen repair method with real-time load monitoring
- Restoration & Cleanup: Backfilling, grading and landscape reinstatement
- Final Inspection & Warranty: Confirming performance and providing service guarantee
What Do New Jersey Homeowners Say? Customer Testimonials and Case Studies
Homeowners regularly praise our prompt diagnostics and lasting repairs.
“Our basement walls were bowing and cracking after heavy rains—within two days of helical pier installation, moisture stopped and cracks stabilized.”
Another case study shows a five-year warranty underpinning project that prevented renewed settlement despite clay soil shifts. Such stories exemplify our commitment to quality and lasting structural protection.
What Are the Most Frequently Asked Questions About Foundation Repair?
Homeowners commonly seek clarity on repair duration, property value impact, severity risks and minor crack solutions. Addressing these concerns helps set realistic expectations and reduce uncertainty.
How Long Do Foundation Repairs Typically Take?
Most foundation repairs complete within one to five days, depending on method complexity and site access. Minor crack injections and slab jacking often finish in under 48 hours, while underpinning or multiple-pier installations may require three to five days of work plus drying or curing time.
Does Repairing Your Foundation Affect Your Home’s Value?
Investing in foundation repair generally enhances property value by ensuring structural stability and preventing future issues. Real estate professionals note that a documented foundation repair with a transferable warranty can increase buyer confidence and resale appraisal.
How Serious Is a Sinking or Settling Foundation?
Sinking foundations indicate soil support loss and progressive structural compromise. Early signs may be cosmetic, but unchecked subsidence accelerates cracking, wall bowing and uneven floors—posing safety hazards and escalating repair costs. Prompt professional assessment averts severe damage.
Can Minor Cracks Be Repaired Without Major Work?
Minor hairline cracks under 0.3 mm often seal effectively with low-viscosity epoxy or polyurethane injection, halting moisture ingress and preventing crack growth. These non-invasive treatments preserve aesthetics and avoid extensive underpinning when structural integrity remains intact.
Homes suffer fewer problems when maintenance and prompt repairs are paired with expert solutions. For a confident assessment and free foundation consultation in New Jersey, contact Effective Basement Solutions’s certified team for reliable diagnostics, transparent estimates and guaranteed results.

zsx2yl
ik65od