Basement Waterproofing in Englewood NJ: French Drains & Sump Pumps
Basement waterproofing protects homes from water intrusion, mold, and structural damage by controlling groundwater and surface runoff before it affects foundation walls or living spaces. This guide explains common water problems in Englewood, NJ, why they occur in Bergen County soils and weather patterns, and which solutions—like French drains, sump pumps, foundation crack repair, and crawl space encapsulation—deliver lasting protection. Homeowners will learn how to spot early signs of moisture, compare interior versus exterior drainage systems, understand typical cost drivers, and evaluate sump pump and backup options that keep basements dry during storms and power outages. The article walks through repair and preventative strategies, provides clear comparison tables for French drains, pumps, and costs, and outlines practical maintenance steps and smart-monitoring choices for long-term resilience. Read on for actionable inspection checklists, EAV-style cost and system tables, and targeted recommendations to help you decide when to schedule an inspection or request a free consultation to diagnose site-specific issues.
What Are the Common Basement Water Problems in Englewood NJ?
Basement water problems in Englewood often stem from a combination of hydrostatic pressure, surface runoff, plumbing leaks, and condensation due to local soil composition and seasonal rainfall patterns. Hydrostatic pressure occurs when groundwater builds against foundation walls and forces moisture through cracks or porous masonry, while surface runoff collects at low points because some lots in Bergen County have poor grading. Plumbing leaks and intermittent roof/downspout failures create localized seepage that worsens mold and finishes deterioration. Understanding these mechanisms helps homeowners prioritize corrective measures and plan inspections that address both source and symptom, which we’ll examine next with practical detection tips.
This list summarizes the most frequent water intrusion mechanisms Englewood homeowners encounter and the immediate remedies to consider.
- Hydrostatic pressure forcing water through foundation joints or cracks; install drainage and reduce groundwater.
- Surface runoff collecting at foundation perimeters; regrade, extend downspouts, or add exterior drains.
- Plumbing leaks from supply or sewer lines inside walls or slabs; inspect and repair plumbing promptly.
- Condensation and high humidity causing damp finishes and mold; add dehumidification and improve ventilation.
- Seepage through porous block or brick foundations; consider interior drain systems or exterior waterproofing.
These problem categories highlight that a single symptom can have multiple causes; identifying the primary driver leads to more effective, longer-lasting solutions and informs whether interior or exterior methods are most appropriate.
How Does Water Damage Affect Basement and Foundation Integrity?
Water damage undermines foundation integrity through sustained exposure to moisture, which accelerates material deterioration and changes soil load-bearing behavior. Hydrostatic pressure pushes soil moisture against footings, increasing lateral forces that can cause cracks, bowing walls, and differential settlement; these effects compound over time and can require costly structural repairs if unaddressed. Moisture also promotes mold growth and rot in framing or finishes, hurting indoor air quality and habitability while decreasing home value. Recognizing how water converts minor stains into structural risk makes early intervention—drainage installation, crack sealing, and active sump systems—both a protective and cost-saving choice for homeowners.
What Signs Indicate a Wet Basement or Mold Growth?
Early detection of moisture and mold prevents escalation from cosmetic damage to structural problems and health concerns. Common observable signs include water stains along the base of walls, peeling paint or plaster, white crystalline efflorescence on masonry, and musty odors that indicate persistent dampness. Additional physical clues are warped or loose floor tiles, damp carpeting, visible mold patches, and rising indoor humidity readings that remain elevated despite ventilation. If any of these indicators appear, immediate steps are inspection, temporary dehumidification, and scheduling a professional evaluation to determine whether drainage, repair, or remediation is required.
How Much Does Basement Waterproofing Cost in Englewood NJ?
Basement waterproofing costs vary by the scope of work, site access, soil and groundwater conditions, and whether the approach is interior, exterior, or a combination. Typical projects include interior French drain installation systems connected to a sump pump, exterior excavation and membrane installation, foundation crack repair, crawl space encapsulation, and sump pump and battery-backup installation; each service carries different material and labor intensities. Cost drivers include the need for excavation, structural repairs, permit requirements, and drainage discharge routing; understanding these factors helps homeowners interpret estimates and compare ROI for preventative vs. reactive work. The table below breaks down common services, typical cost ranges, and primary cost factors to guide budgeting and decision-making.
The following EAV-style table compares common waterproofing services, average cost ranges, and the main variables that affect pricing.
| Service | Typical Cost Range | Primary Cost Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Interior French drain + sump pump | $2,500 – $10,000 | Basement finishing, excavation length, sump pump type |
| Exterior waterproofing & membrane | $8,000 – $20,000 | Excavation depth, soil removal, yard restoration |
| Foundation crack repair | $500 – $6,000 | Crack length, structural vs non-structural, access |
| Crawl space encapsulation | $2,000 – $8,000 | Area size, vapor barrier quality, dehumidifier inclusion |
This breakdown shows that interior solutions are often less disruptive upfront, while exterior approaches address the source but cost more; selecting the right option depends on site conditions, long-term priorities, and budget.
What Factors Influence Basement Waterproofing Pricing?
Several site-specific attributes materially influence contractor estimates and timelines, and recognizing these drivers helps homeowners evaluate competing quotes. Key factors are soil type and groundwater table height—silty or clay-rich soils retain water and increase excavation difficulty—property grading and drainage access, presence of finished basement areas that require restoration, and whether structural repairs are needed before waterproofing can proceed. Accessibility, permits, and required tie-ins to storm systems or daylighting points also add time and cost. Asking contractors to itemize these elements clarifies the estimate and highlights which actions produce the most risk reduction per dollar.
Below is a short checklist-style EAV mini-table summarizing pricing drivers and their typical impact on costs.
| Factor | Typical Impact on Cost | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Soil type & water table | High | Harder excavation and continuous seepage increase scope |
| Finished basement restoration | Medium-High | Repairing finishes raises total project cost |
| Structural repairs | High | Requires engineering and specialized labor |
| Access & landscaping impact | Medium | Yard restoration and confined access increase labor |
Recognizing these influences enables homeowners to prioritize preventative measures and request estimates that compare like-for-like scopes.
How Does Preventative Waterproofing Save Money Long-Term?
Preventative waterproofing reduces the likelihood of emergency repairs, mold remediation, and structural remediation that can be far more expensive over a home’s lifetime. By addressing drainage and moisture sources early—through improved grading, functioning downspouts, and proper sub-surface drainage—homeowners lower recurring maintenance and insurance exposure while preserving interior finishes and HVAC efficiency. Case comparisons typically show that investing in a comprehensive waterproofing approach can halve the long-term expense of repeated patch repairs and mold abatement over a decade. Prioritizing preventative work also boosts resale value and buyer confidence in markets where basements are common, making the upfront investment financially prudent.
If you’d like a site-specific evaluation, request a free estimate or consultation so a local specialist can assess soil, grading, and foundation conditions and provide a customized cost projection tailored to your home’s needs.
What Are the Benefits and Types of French Drain Installation in Englewood NJ?
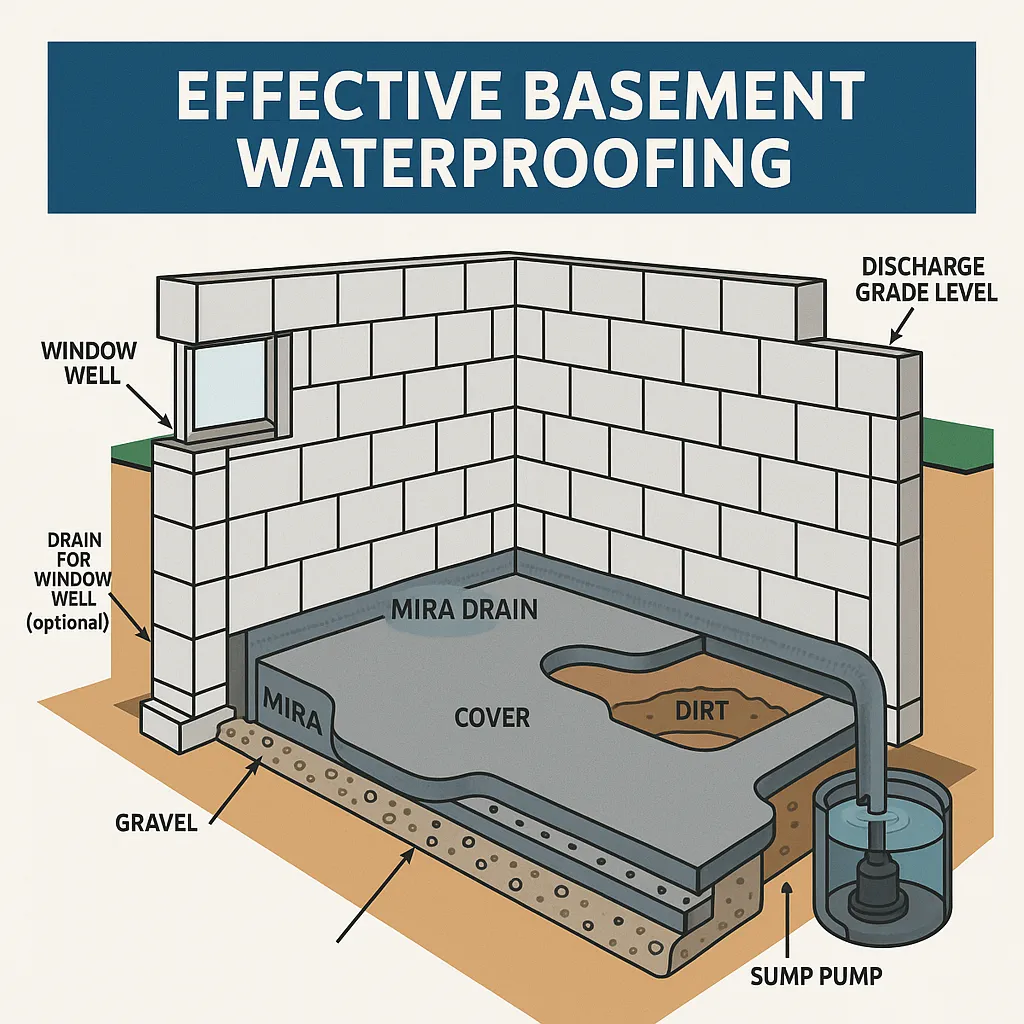
A French drain redirects groundwater away from foundation footings using a perforated pipe surrounded by gravel and a route to a discharge point, relieving hydrostatic pressure and preventing seepage. Benefits include reduced wall seepage, lower interior humidity, protection of finishes and stored items, and improved foundation longevity by lowering lateral loads. French drains come in interior and exterior forms—each has advantages, trade-offs, and situations where they excel—so choosing between them depends on site-specific drainage sources and homeowner disruption tolerance. Below is a comparison table that clarifies installation location, pros, and cons to help homeowners decide.
This table compares interior and exterior French drain options and summarizes when each approach is recommended.
| Drain Type | Installation Location | Pros / Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Interior French drain | Inside basement along footing | Pros: less yard disruption, faster install. Cons: may require finish repair, treats symptoms not always source. |
| Exterior French drain | Outside footing, below grade | Pros: addresses source, prevents saturation. Cons: higher cost, extensive excavation. |
| Sub-slab drain | Under concrete slab | Pros: protects slab from under-slab pressure. Cons: invasive, often used during major renovations. |
The comparison shows that interior systems are cost-effective for managing interior seepage, while exterior drainage addresses the root cause when yard grading or high water tables are primary drivers; professional inspection clarifies the best match for your property.
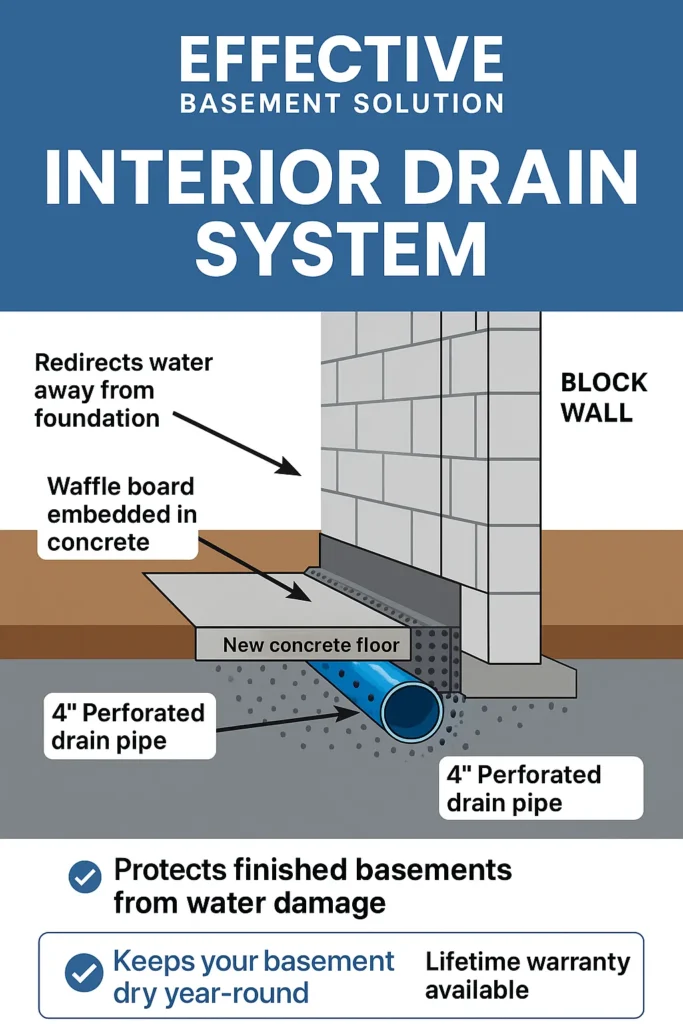
How Do Interior and Exterior French Drains Work?
Interior French drains are installed by cutting a narrow trench along the basement perimeter at the foundation footing, placing perforated pipe in gravel, and channeling water to a sump pit where a pump discharges it away from the home. Exterior drains require excavation to the footing level, placement of a draining trench lined with filter fabric and gravel, installation of perforated pipe, and regrading or daylighting to move water away from the structure. Interior systems are less disruptive to landscaping and often quicker to install, while exterior systems are more permanent because they stop saturation before it reaches the foundation wall. Choosing between them depends on access, finish restoration plans, and whether the primary goal is symptom control or source elimination.
For many Englewood properties with high groundwater or widespread yard runoff, a combined approach—exterior drainage where feasible and interior systems for immediate relief—delivers the most durable outcome, and professional inspection helps tailor the mix.
When Is French Drain Installation Necessary for Your Home?
French drain installation is recommended when homeowners experience chronic seepage along the foundation, recurring sump pump activation after storms, visible hydrostatic-related cracking, or persistent high basement humidity despite temporary fixes. Other triggers include recent landscape changes that altered grading, neighbors with similar issues suggesting a high local water table, or failed previous repairs that did not address sub-surface drainage. A thorough inspection that includes soil observations, water table assessment, and review of downspout effectiveness clarifies whether a French drain (interior, exterior, or sub-slab) is the appropriate long-term solution. When in doubt, a targeted inspection and free consultation can identify the most effective choice for your site and budget.
For homeowners considering installation, note that professional inspections and tailored installation plans are available via a free consultation to determine the right drain type and discharge strategy for your property.
How Do Sump Pumps Protect Basements and What Are Installation Options in Englewood NJ?
A sump pump protects basements by collecting groundwater that enters a sump pit and actively discharging it away from the foundation, preventing pooling and reducing hydrostatic pressure. Sump pumps reduce the risk of flooding during heavy rain, protect finishes and stored items, and work in tandem with drainage systems to keep basements dry. Installation options include pedestal pumps, submersible pumps, and models paired with battery or water-powered backups to maintain protection during power outages. Choosing the correct pump type considers pit size, expected flow rates, and backup strategies to ensure continuous operation during storms that commonly coincide with power interruptions.
The following EAV table outlines pump types, typical power sources, and expected lifespan and backup considerations to aid selection.
| Pump Type | Power Source | Typical Lifespan / Backup Options |
|---|---|---|
| Pedestal pump | AC power (motor above sump) | 7–10 years; simpler motor access; battery backup recommended |
| Submersible pump | AC power (immersed) | 7–15 years; quieter; battery backup commonly added |
| Battery backup pump | Battery + AC | Provides hours of runtime during outage; battery lifespan 3–5 years |
| Water-powered backup | Municipal water | Operates without electricity; depends on municipal supply and pressure |
This table illustrates trade-offs: submersible pumps are compact and powerful, pedestal units are easier to service, and battery or water-powered backups add critical resilience during storm-induced outages.
What Are the Signs You Need Sump Pump Repair or Replacement?
Recognizing sump pump distress early prevents basement flooding and expensive damage; common signs include the pump failing to start during heavy rain, continuous running without cycling off, loud or unusual noises indicating motor stress, and visible corrosion or leaks around the unit. Frequent short-cycling shortens pump life and suggests float switch or sizing problems, while failure to operate during tests indicates electrical or motor issues. If any of these symptoms are present, immediate inspection, testing, and, if needed, replacement with a correctly sized pump and a recommended backup system are prudent to restore reliable flood protection and reduce future emergency risk.
What Are the Benefits of Battery Backup Sump Pumps?
Battery backup sump pumps supply critical hours of operation during power outages, which often coincide with heavy storms, and thus sharply reduce the likelihood of basement flooding when main pumps lose power. Typical backup systems provide several hours of runtime depending on battery capacity and pump draw, with routine battery maintenance and periodic replacement every 3–5 years being central to reliable performance. Backup systems can be stand-alone or integrated with smart monitors that send alerts to homeowners about pump status and battery health. Investing in a robust backup solution is a cost-effective mitigation measure in communities with aging grids or frequent severe weather.
How Can Foundation Crack Repair and Crawl Space Encapsulation Improve Home Stability in Englewood NJ?
Foundation crack repair and crawl space encapsulation address both structural integrity and moisture control, delivering complementary benefits that improve long-term home stability and indoor air quality. Crack repair methods like epoxy injection or mechanical stitching restore continuity in masonry or concrete, stop active seepage, and prevent further propagation when underlying settlement or hydrostatic forces are addressed. Encapsulation installs a continuous vapor barrier, seals vents, and often pairs with a dehumidifier to stop ground moisture from entering the living envelope; this reduces mold risk and can improve HVAC efficiency by stabilizing humidity. Combining repairs with drainage and sump systems creates an integrated strategy that reduces future maintenance and preserves home value.
What Causes Foundation Cracks and How Are They Repaired?
Foundation cracks arise from settlement, freeze-thaw cycles, hydrostatic pressure, and soil movement; identifying the cause determines the appropriate repair method. Non-structural hairline cracks often respond well to epoxy injection or polyurethane sealing, while wider or moving cracks may require structural techniques like carbon fiber reinforcement, underpinning, or helical tiebacks under the guidance of an engineer. Repair timelines depend on access and weather, but addressing drainage and soil moisture concurrently prevents recurrence. Monitoring crack width changes over time helps determine whether cosmetic or structural intervention is necessary, and professionals can recommend the minimally invasive solution that restores performance.
How Does Crawl Space Encapsulation Prevent Moisture and Mold?
Crawl space encapsulation prevents moisture and mold by installing a continuous vapor barrier on the ground and walls, sealing vents and penetrations, and adding dehumidification and conditioned air where appropriate. The barrier blocks ground moisture migration, while sealing reduces warm-air infiltration that causes condensation; together they lower relative humidity and stop mold-friendly conditions. Benefits include improved indoor air quality, reduced pest entry, and better energy performance because conditioned air leakage is minimized. Regular inspections and dehumidifier maintenance keep the system effective and extend the lifespan of sub-surface structures, making encapsulation a high-value component of a comprehensive moisture-control plan.
What Flood Protection Systems Are Available for Basements in Englewood NJ?
Basement flood protection systems range from passive barriers to active removal devices, and choosing the right combination responds to local watershed, grading, and groundwater conditions. Passive options include flood panels or removable barriers for doorways and low openings, and waterproofing membranes applied to foundation walls to block seepage. Active systems focus on water removal through interior French drains and sump pumps, often enhanced with battery-backup or smart monitoring to ensure operation during outages. Other measures—check valves on sewer lines, downspout extensions, and regrading—reduce external water sources. Combining methods into an integrated plan matches the severity and source of risk to the most effective defenses.
- Flood panels and door seals: Best for entry points prone to flash runoff and sewer backup.
- Waterproof membranes and exterior drainage: Ideal where exterior saturation and high water table drive seepage.
- Interior drainage + sump pump systems: Effective for active removal and protecting finished basements.
- Backflow preventers and check valves: Necessary when sewer backup is a local risk factor.
Selecting an appropriate combination depends on whether water enters from the ground, surface runoff, or utilities; professional assessment prioritizes the most cost-effective measures.
How Do Basement Flood Protection Systems Work?
Flood protection systems either block entry or actively remove water: barriers and membranes prevent ingress, while drains and pumps collect and discharge it away from the foundation. Passive systems rely on impermeable layers or physical barriers to resist water pressure, making them suitable for predictable surge scenarios, whereas active systems respond to accumulated water and pump it out to reduce standing volumes. Integrating both approaches—sealing vulnerabilities and ensuring reliable removal—addresses both prevention and response, which is especially important in properties subject to sudden intense storms. Maintenance, testing, and periodic component replacement keep these systems ready for high-risk events.
What Local Environmental Factors Increase Flood Risk in Englewood NJ?
Englewood’s flood risk is influenced by Bergen County’s soil types, which can include clay-rich layers that retain water, local topography that creates low-lying collection points, and increasing heavy-rainfall events that saturate soil and overwhelm surface drainage. Lot grading that slopes toward foundations, undersized or blocked storm drains, and nearby impervious surfaces accelerate runoff toward homes. Seasonal freeze-thaw cycles and spring snowmelt can also raise groundwater levels and worsen hydrostatic pressure on foundations. Prioritizing inspection of grading, downspouts, and nearby drainage infrastructure clarifies whether site-specific interventions—regrading, exterior drains, or sump upgrades—are necessary to reduce flood exposure.
If you’d like a focused assessment that connects these local factors to a recommended protection plan, request a free consultation to get a tailored evaluation and cost estimate for solutions matched to your property.

0my8qb